NetBIOS Name Service (NBNS)

NBNS
NetBIOS Name Service
NBNS used in Windows-based networks to translate NetBIOS computer names to IP addresses.
Port: 137 UDP | RFC:1001
OSI Layer: 6 ( Session layer)
Cyber Security Stance:
Designed by Vivekanand Padala
Protocol Overview
NETBIOS-NS is part of the NetBIOS protocol suite, which was developed by Microsoft in the 1980s as a way to allow Windows-based computers to communicate with each other in a networked environment.
NetBIOS-NS uses User Datagram Protocol (UDP) as its transport protocol and operates on port 137. When a device needs to resolve a NetBIOS name, it sends a broadcast message to the network asking for the IP address associated with that name. The device that is hosting the NetBIOS name will respond with its IP address, allowing the requesting device to establish a connection.
Although NetBIOS-NS is an important protocol for early versions of Windows and some legacy applications, it has some security vulnerabilities and is not typically used on modern networks. Many modern operating systems have replaced NetBIOS-NS with more secure and efficient protocols, such as DNS or the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP).
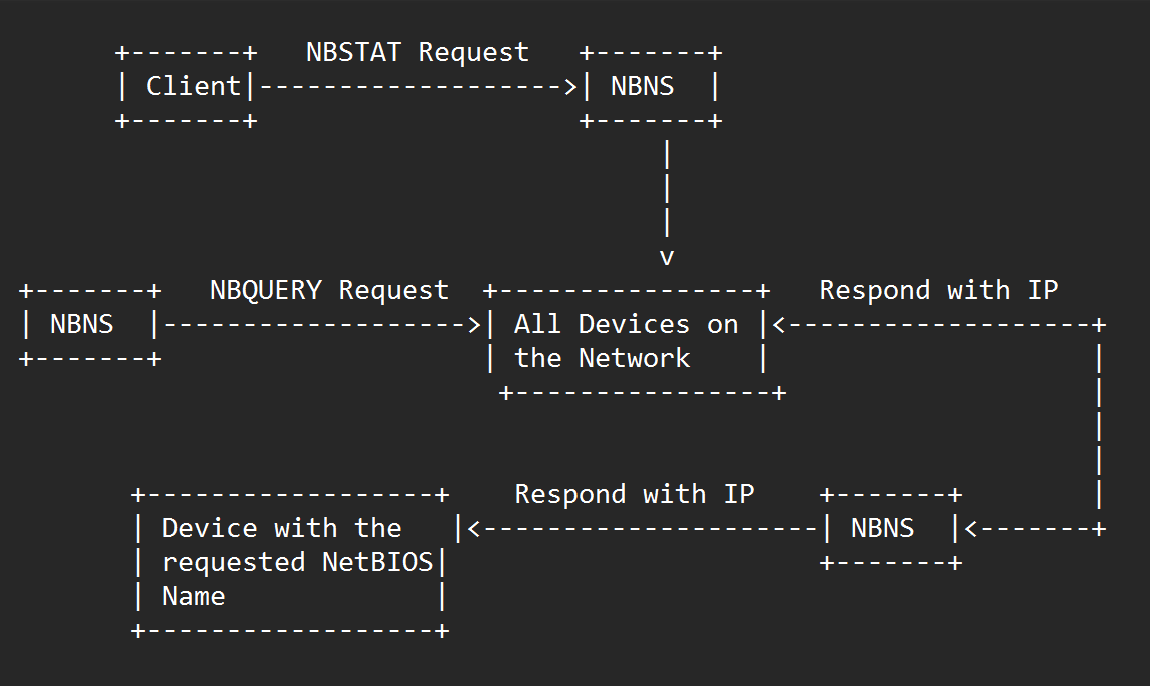
NBNS workflow
- The client sends a NetBIOS name query request (NBSTAT) to the NBNS server. The NBSTAT request contains the NetBIOS name of the destination device that the client wants to communicate with.
- The NBNS server receives the NBSTAT request and checks its local NetBIOS name cache to see if it has a matching IP address for the requested NetBIOS name. If it finds a match, it responds to the client with the IP address.
- If the NBNS server does not have a matching IP address in its local cache, it broadcasts a NetBIOS name query request (NBQUERY) to all devices on the network.
- The device that has the requested NetBIOS name responds to the NBQUERY request with its IP address.
- The NBNS server receives the response from the device and caches the NetBIOS name and IP address mapping in its local cache for future use.
- The NBNS server responds to the original NBSTAT request from the client with the IP address it received from the device that responded to the NBQUERY request.
- The client can now use the IP address to establish a connection with the destination device.