Server Message Block (SMB)

SMB
Server Message Block
SMB is a network file sharing protocol commonly used by Windows operating systems.
Port: 445 TCP/UDP | RFC: N/A
OSI Layer: 7 (Application Layer)
Cyber Security Stance:
Designed by Vivekanand Padala
Protocol Overview
SMB is a network file sharing protocol that enables clients to read, write, and execute files on a remote server.
SMB uses a client-server model, where a client machine sends requests to a server machine over a network connection. The server then responds to these requests and provides the client with access to shared files and resources.
SMB is an important protocol for Windows-based networks, and it has been widely adopted by other operating systems as well. However, SMB has also been the target of several security vulnerabilities over the years, and it is important to ensure that SMB-based file sharing is configured securely to minimize the risk of unauthorized access or data theft.
- Authentication. SMB provides a way for clients to authenticate with a server, typically using a username and password.
- File and printer sharing. SMB allows clients to access shared files and printers on a server.
- Directory services. SMB can be used to browse and query directory services, such as Active Directory.
- Transport security. SMB can be configured to use encryption and signing to protect data transmitted over the network.
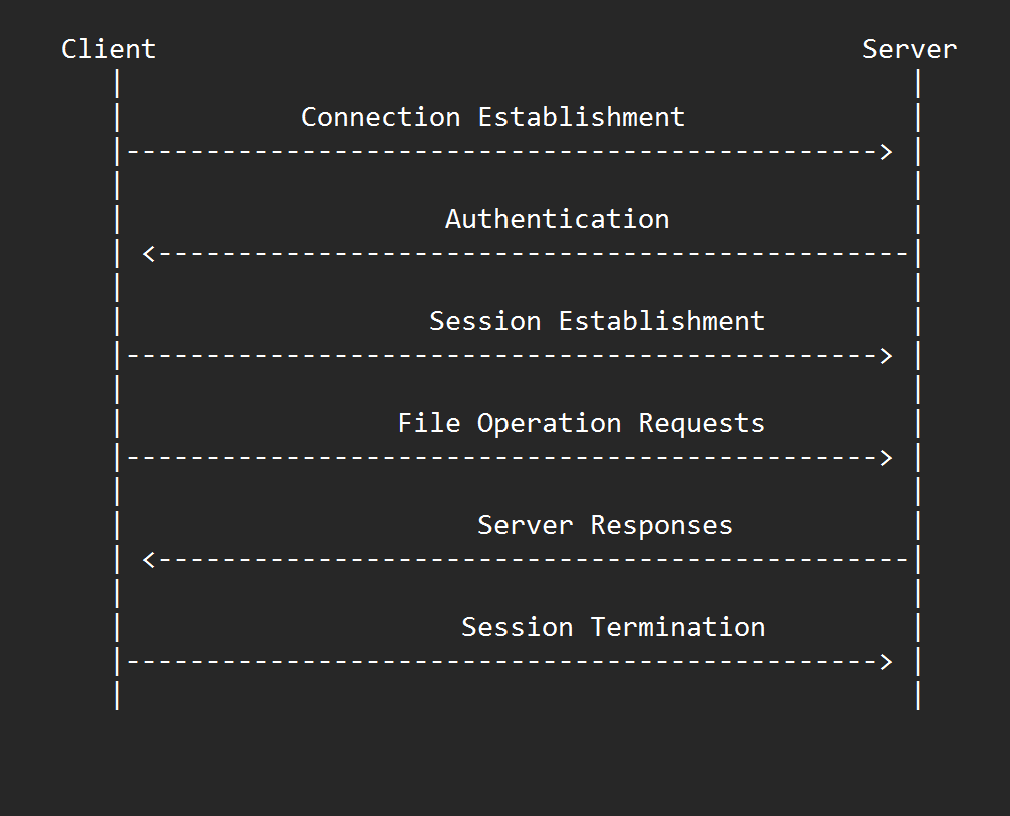
SMB workflow
- Connection Establishment. The client establishes a TCP connection to the server using the server's IP address and port number 445.
- Authentication. The client sends authentication information to the server, which verifies the client's identity and credentials. Authentication can be done using various methods, including password authentication and public key authentication.
- Session Establishment. Once authenticated, the client and server establish a session by exchanging negotiation messages to determine the protocol version, security settings, and other parameters.
- File Operation Requests. The client sends requests to the server to read, write, or modify files and directories. These requests include the file name, access mode, and other parameters.
- Server Responses. The server responds to the client's requests with the requested file data or an error message if the file cannot be accessed.
- Session Termination. When the client is finished with the session, it sends a message to the server to terminate the session and close the connection.